
Structure of Atom Class 11 Notes Chemistry Leverage Edu
In this video we cover the structure of atoms, what are subatomic particles, energy levels, and stable and reactive atoms.Transcript and notesAtomic structur.
What is Electricity?
By convention, elements are organized in the periodic table, a structure that captures important patterns in their behavior.Devised by Russian chemist Dmitri Mendeleev (1834-1907) in 1869, the table places elements into columns—groups—and rows—periods—that share certain properties.These properties determine an element's physical state at room temperature—gas, solid, or liquid.
Atoms, Molecules, and Compounds What's the Difference? Owlcation
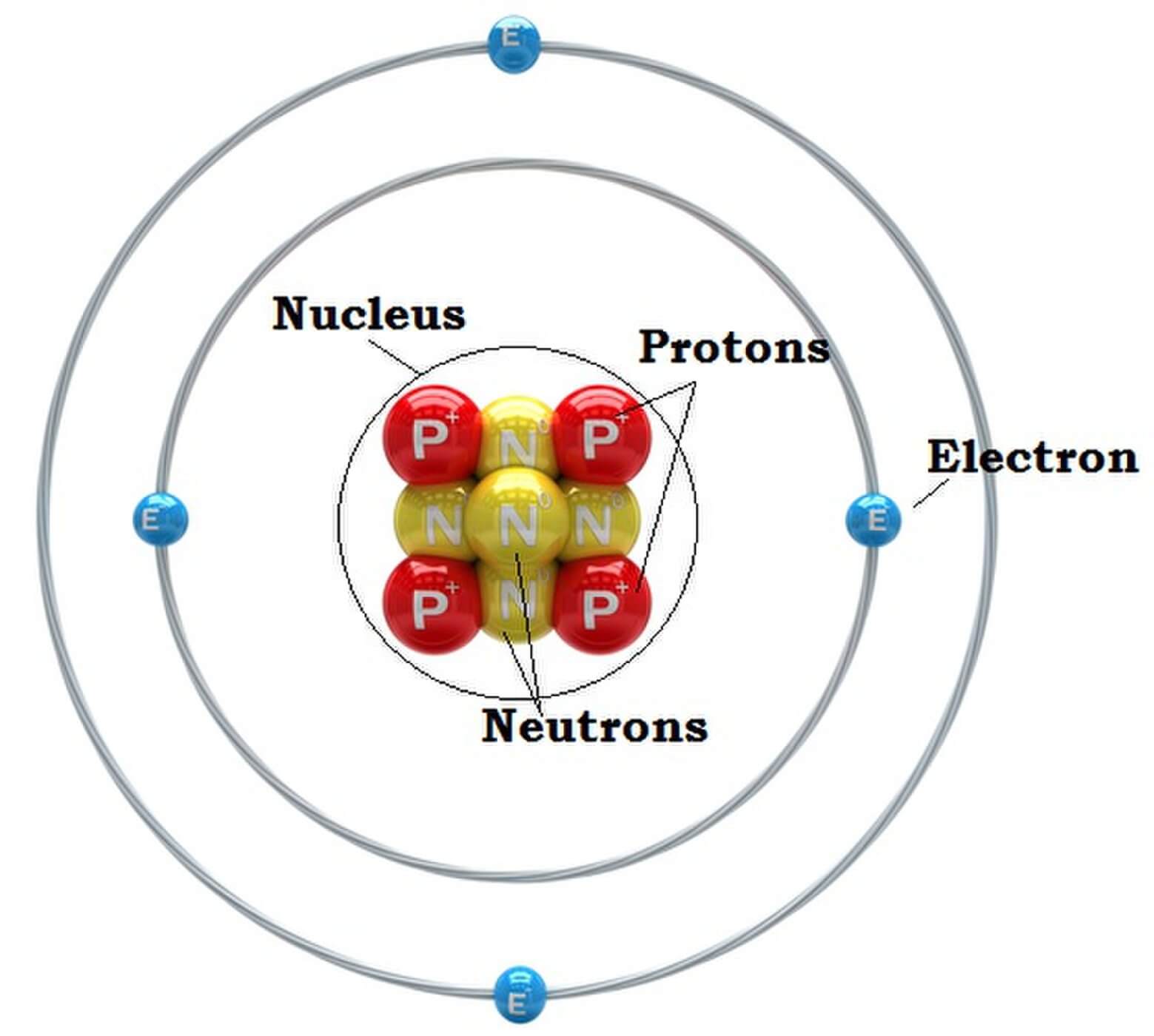
Parts of an Atom An atom consists of two parts. These are the nucleus and extranuclear portions. The nucleus is present in the centre of the atom and is surrounded by the extranuclear portions. The radius of the nucleus of an atom is nearly 10 - 15 m, while that of the atom is 10 - 10 m.
Atom Definition, Structure & Parts with Labeled Diagram
Structure of atom | Khan Academy Physical Chemistry (Essentials) - Class 11 8 units · 52 skills Unit 1 Welcome to physical chemistry Unit 2 Structure of atom Unit 3 Some basic Concepts of Chemistry Unit 4 Redox reactions Unit 5 Gaseous state Unit 6 Thermodynamics Unit 7 Chemical Equilibrium Unit 8 Ionic equilibrium Course challenge
What is an Atom? Definitions & Examples Let us learn Basics News Bugz
Here are electron shell atom diagrams for the elements, ordered by increasing atomic number . For each electron shell atom diagram, the element symbol is listed in the nucleus. The electron shells are shown, moving outward from the nucleus.
/GettyImages-141483984-56a133b65f9b58b7d0bcfdb1.jpg)
Basic Model of the Atom Atomic Theory
The structure of the atom An atom is the smallest unit of matter that retains all of the chemical properties of an element. For example, a gold coin is simply a very large number of gold atoms molded into the shape of a coin, with small amounts of other, contaminating elements.
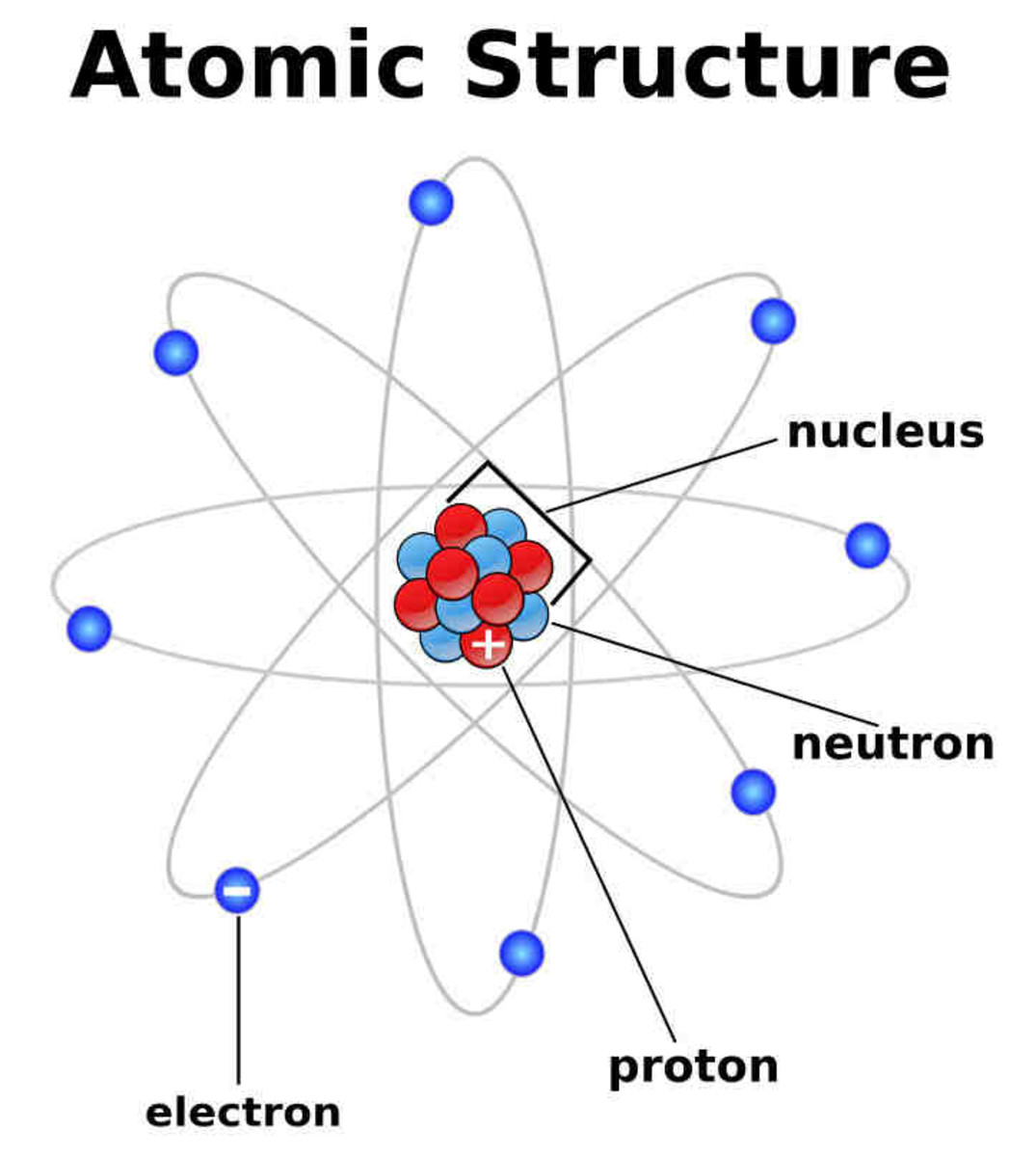
Atoms and Atomic Structure HubPages
The structure of a carbon atom, not drawn to scale The masses close mass The amount of matter an object contains. Mass is measured in kilograms (kg) or grams (g). of subatomic particles are very tiny.
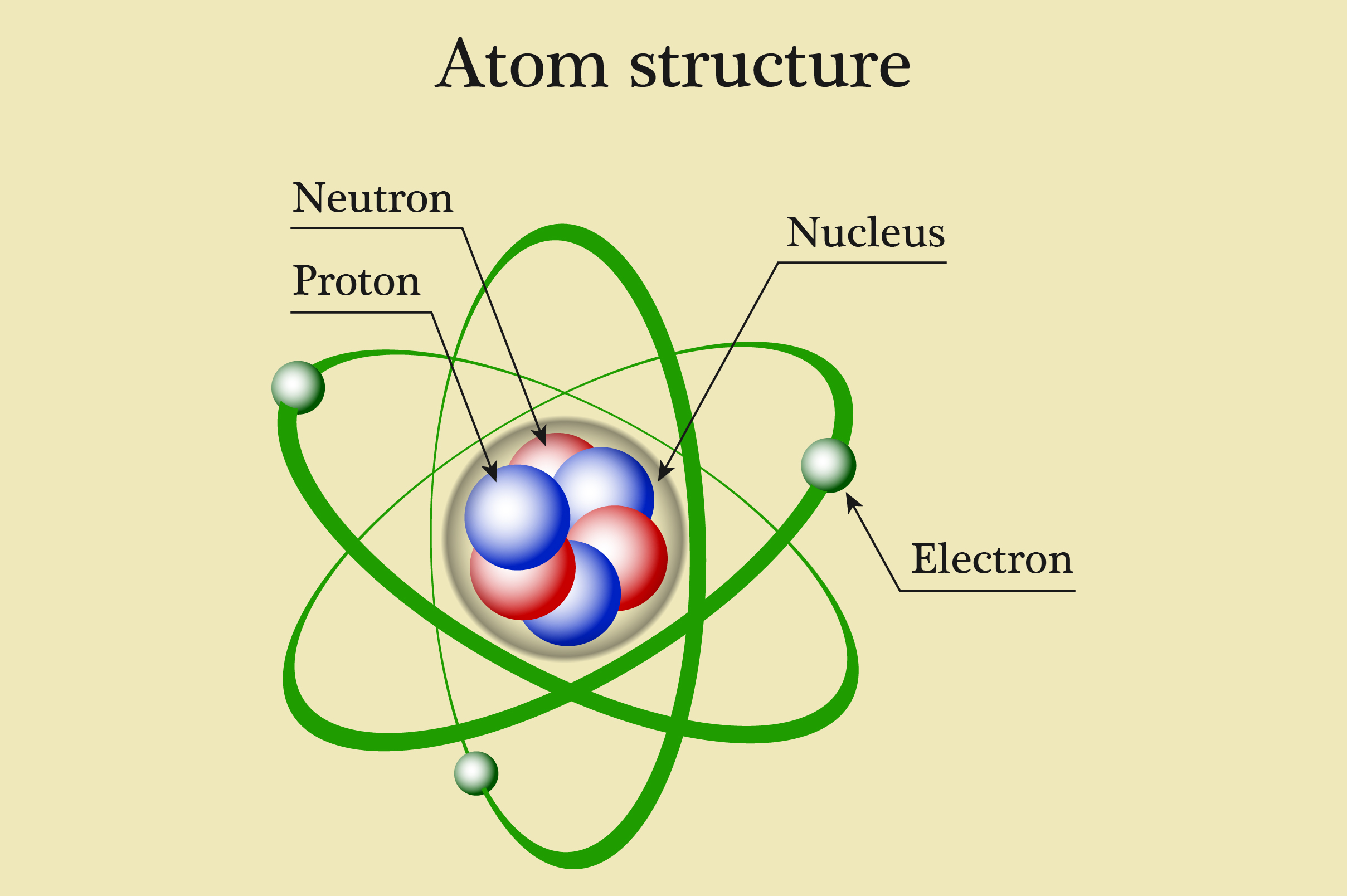
What Is An Atom Atoms Today, atomic research is focused on studying the structure and the
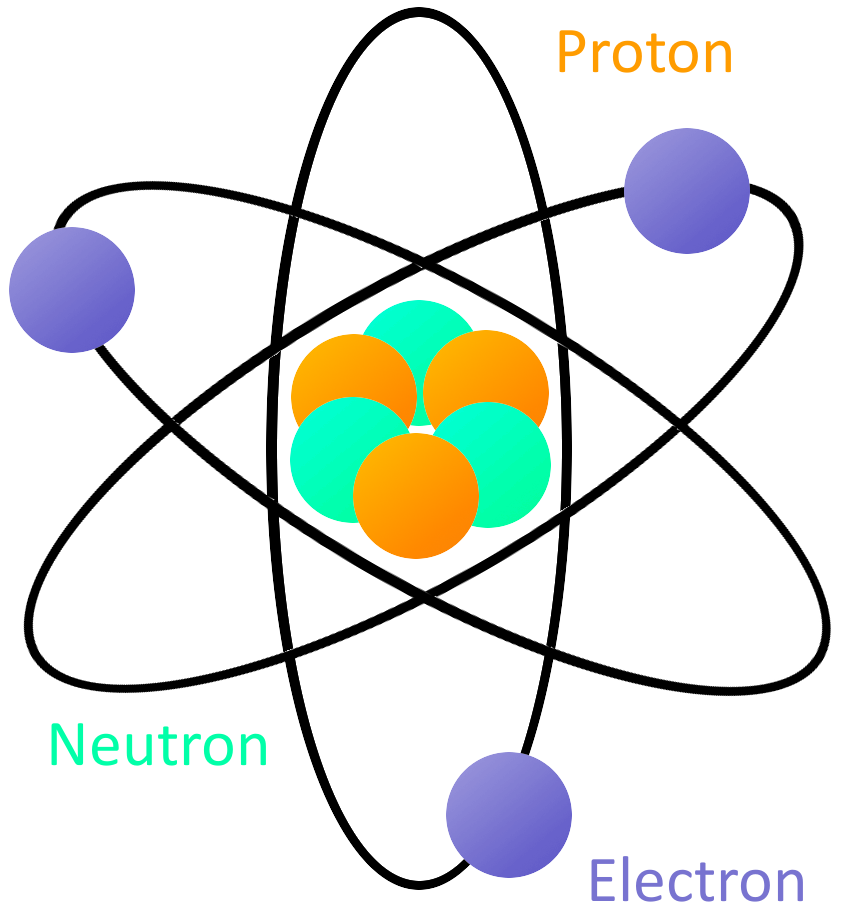
Most of the atom is empty space. The rest consists of three basic types of subatomic particles: protons, neutrons, and electrons.The protons and neutrons form the atom's central nucleus. (The ordinary hydrogen atom is an exception; it contains one proton but no neutrons.) As their names suggest, protons have a positive electrical charge, while neutrons are electrically neutral—they carry.
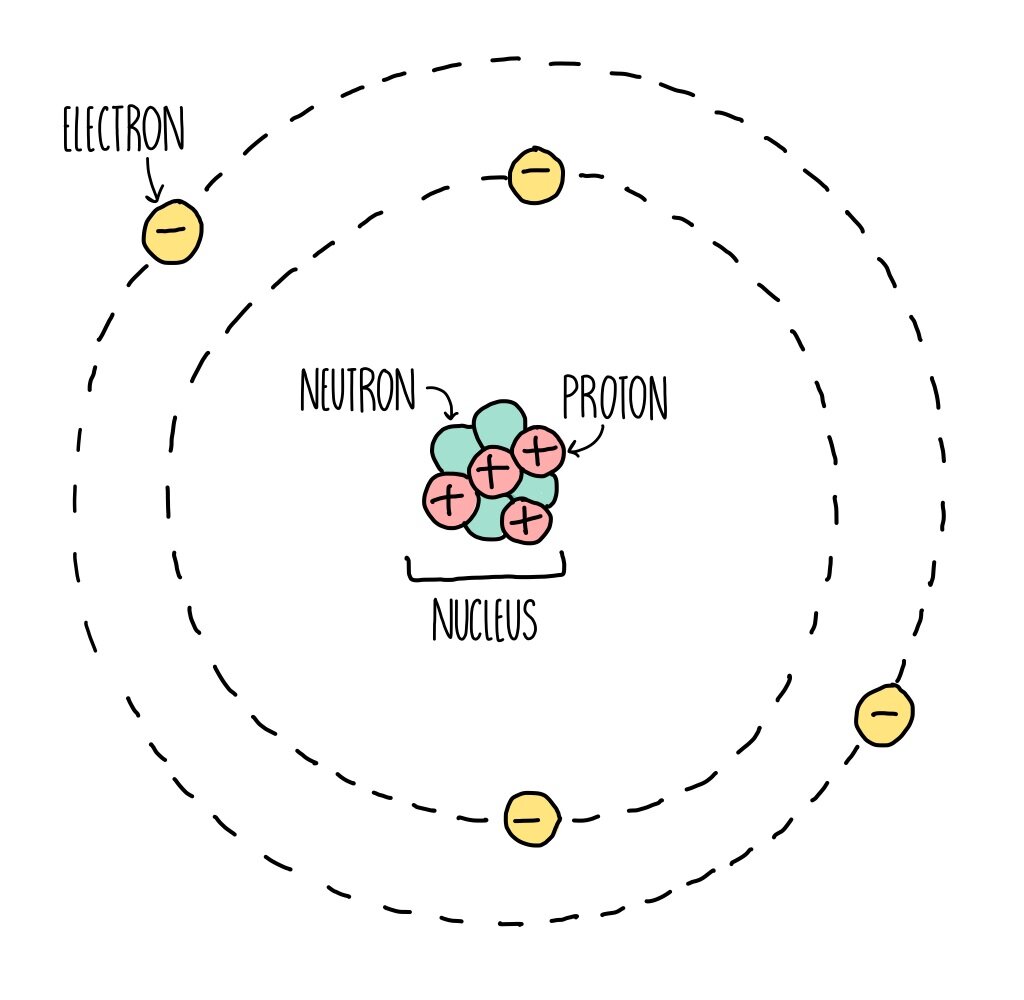
Atomic Structure (GCSE) — the science hive
An atom consists of a nucleus of protons and generally neutrons, surrounded by an electromagnetically-bound swarm of electrons. The chemical elements are distinguished from each other by the number of protons that are in their atoms. For example, any atom that contains 11 protons is sodium, and any atom that contains 29 protons is copper.

Atomic Structure Broad Learnings
An atom is composed of two regions: the nucleus, which is in the center of the atom and contains protons and neutrons, and the outer region of the atom, which holds its electrons in orbit around the nucleus. Protons and neutrons have approximately the same mass, about 1.67 × 10 -24 grams, which scientists define as one atomic mass unit (amu.

Chemical bonding Atomic structure and bonding Britannica
Single-atom catalysts (SACs) have received extensive attention in the fields of electrocatalytic sensing, and in response to the requirements of different sensing systems, a variety of metal single-atom structures have been emerged.. and then focus on the structural regulation strategies of SACs and the structure-performance relationship.

Learn the Parts of an Atom
The relationship between orbital energies and orbital states for the hydrogen atom can be seen in Figure 22.11. Figure 22.11 Energy-level diagram for hydrogen showing the Lyman, Balmer, and Paschen series of transitions. The orbital energies are calculated using the above equation, first derived by Bohr.
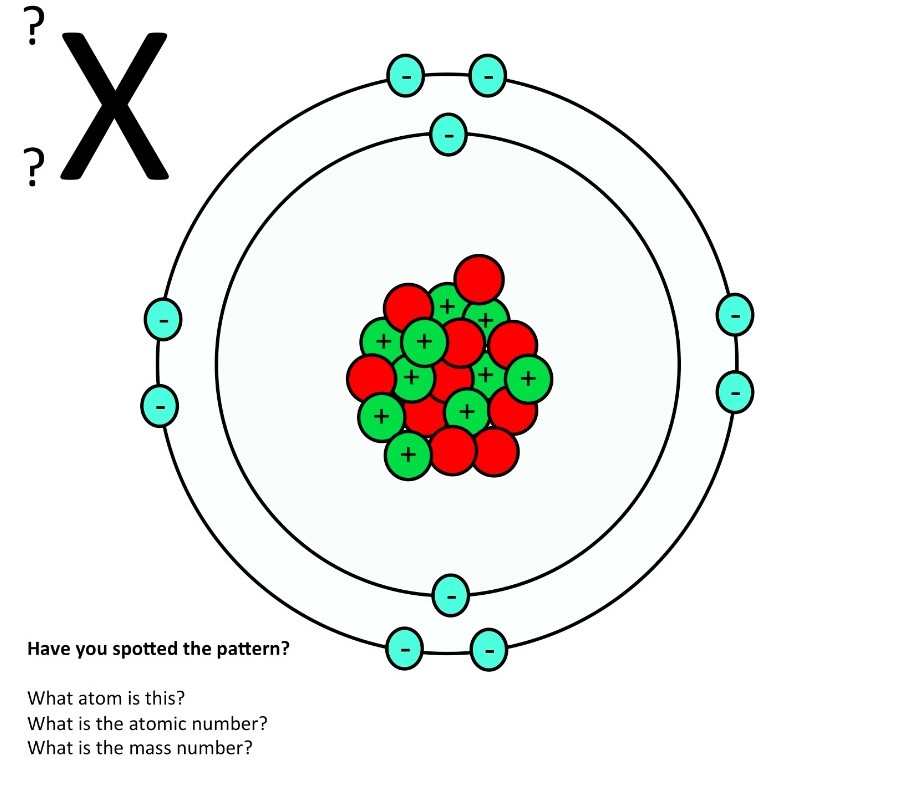
Atomic structure teaching resources the science teacher
Introduction to the atom Google Classroom About Transcript Learn how atoms are made up of protons, neutrons, and electrons. Elements are defined by the atomic number, the number of protons in the nucleus. The mass of an atom is determined by the total number of protons and neutrons. Created by Sal Khan. Questions Tips & Thanks
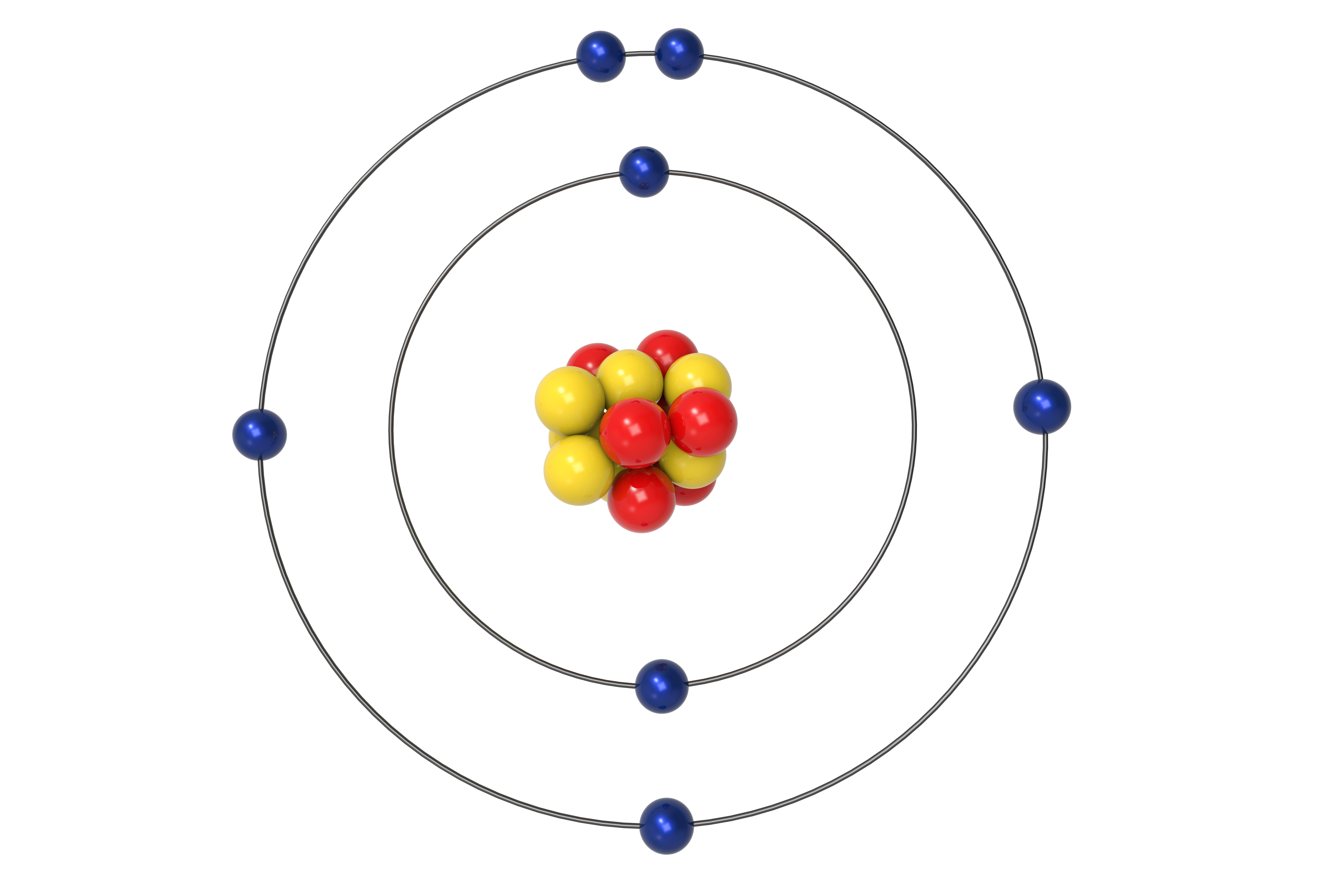
Subatomic Makeup Of An Atom Makeupview.co
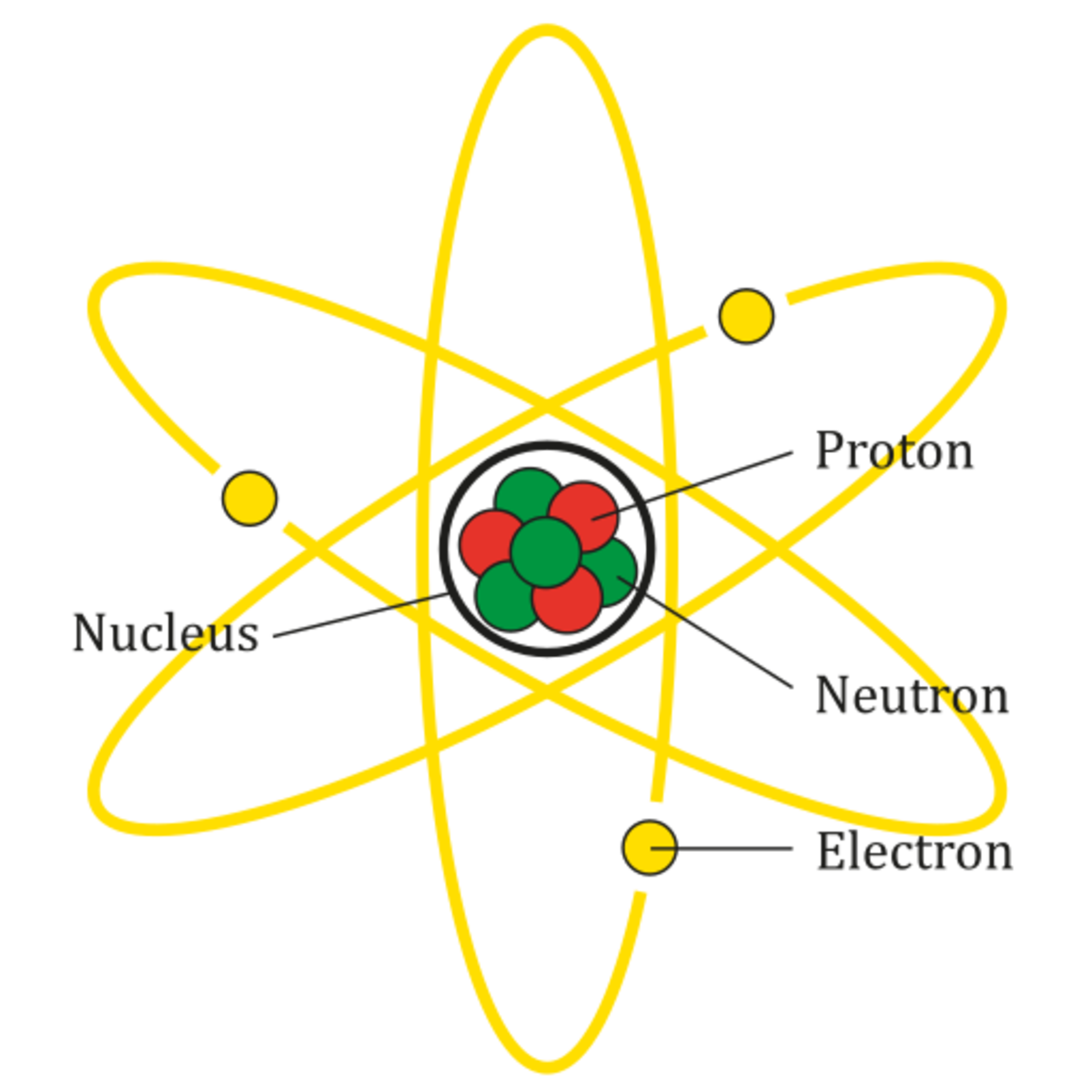
Atom February 17, 2010 by Jerry Coffey Atom Diagram [/caption]The image on the left is a basic atom diagram. This one shows the protons, neutrons, and electrons of a carbon atom. Each is in.

The Structure of the Atom GCSE Physics Science) AQA Revision Study Rocket
The classical "planetary" model of an atom. The protons and neutrons in the nucleus are circled by electrons in "orbit" around the nucleus. The number of protons determines which element is represented, the number of electrons determines its charge, and the number of neutrons determines which isotope of the element is represented.
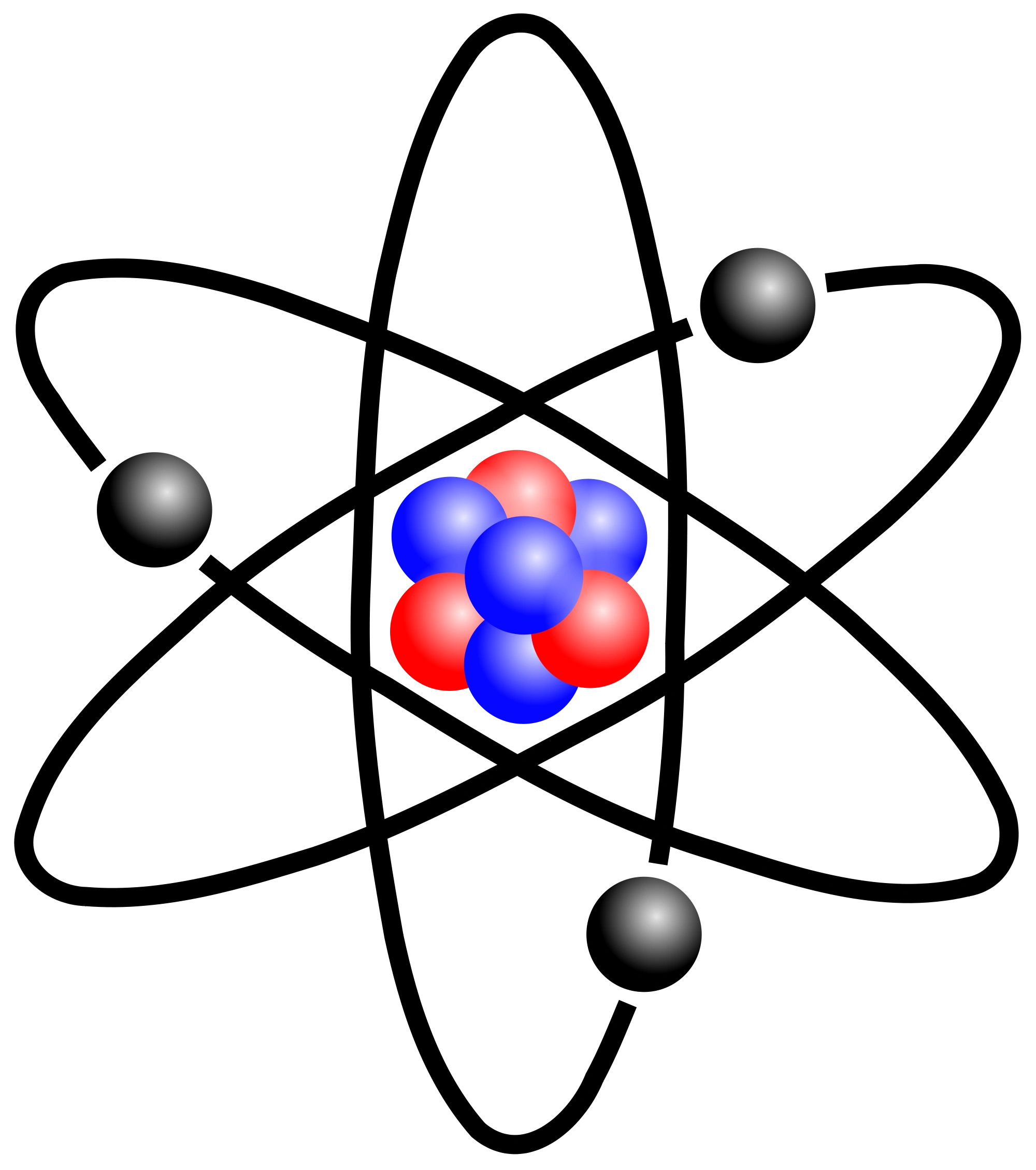
abc blog Discovery of an ATOM.
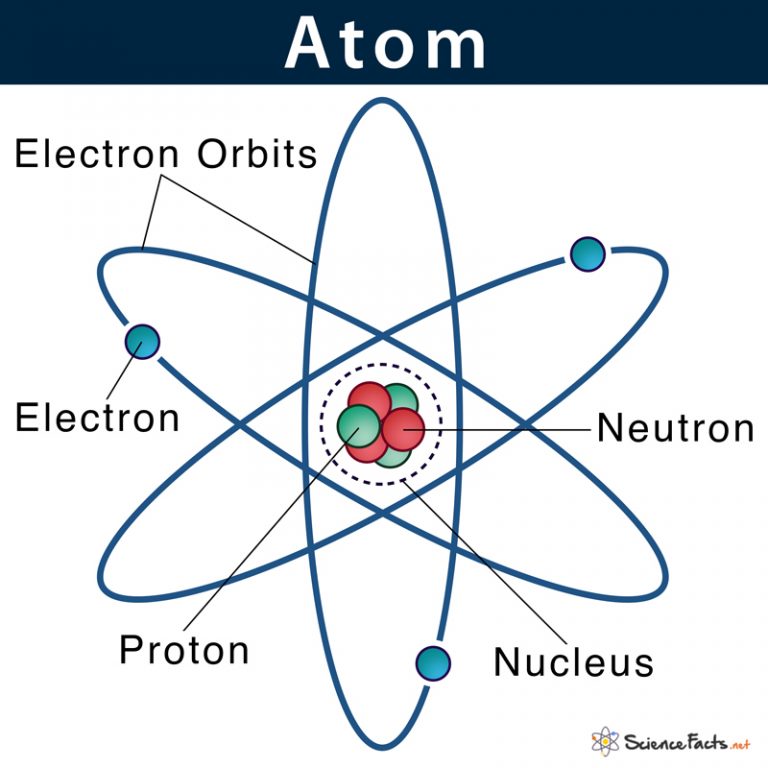
Figure 2.2.1 2.2. 1: The Structure of the Atom. Atoms have protons and neutrons in the center, making the nucleus, while the electrons orbit the nucleus. The modern atomic theory states that atoms of one element are the same, while atoms of different elements are different.